Risk Management
At Dmaze, we understand that effective risk management is critical for organizations to protect against potential losses and improve business outcomes. That's why we've developed a powerful software platform that empowers you to manage your risks with ease.
Our platform combines cutting-edge AI technology with configurable templates to deliver unmatched performance across risk management, audits, strategy management, business processes, governance, control activities, and more!
With Dmaze, you can easily identify and assess risks across your organization. Our platform provides you with a centralized view of your risks, enabling you to prioritize them and develop mitigation strategies that are aligned with your business objectives.
Our AI algorithms work tirelessly behind the scenes to provide you with relevant suggested information that will help you make informed decisions and streamline your workflows. Plus, our configurable templates make it easy to create and manage risk assessments that are tailored to your specific needs.
Whether you're managing risks related to compliance, operations, or financial performance, Dmaze helps you optimize risk management and improve business outcomes. With Dmaze, you can rest assured that your risk management is in safe hands. Discover the power of Dmaze today and take your risk management to the next level!
Introducing Barrier Risk Assessment
Our team is working hard to bring this feature to Dmaze and we can't wait for you to try it out. Stay tuned for updates on it's progress.
Barrier Risk Assessment the way we see it
Barrier risk assessment is a process used to identify potential risks and hazards in a system or process, and to determine the effectiveness of existing barriers in preventing or mitigating those risks.
The process typically involves identifying the various elements of a system that are designed to prevent or control risk, such as physical barriers, procedural controls, and organizational measures. The risk assessment then evaluates the likelihood and severity of potential hazards, and assesses the effectiveness of the existing barriers in reducing or controlling those risks.
The goal of a barrier risk assessment is to identify any gaps in the system's defenses and to recommend improvements to reduce the likelihood and consequences of accidents or incidents. This can help to enhance safety and minimize the potential for harm to people, the environment, or assets.
It is important to note that the barrier risk assessment process is not a one-time event, but rather a continuous process that should be revisited and updated regularly to ensure that the system remains effective in managing risks.
Barrier Risk Assessment Standards
When it comes to barrier risk assessment processes, some of the most relevant standards include: ISO 31000:2018 - Risk management - Guidelines: This standard provides principles and guidelines for effective risk management. It is useful in developing an overall risk management framework for an organization. ISO 27001:2013 - Information technology - Security techniques - Information security management systems - Requirements: This standard provides requirements for an information security management system (ISMS). It can be used to assess risks related to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. IEC 61511:2016 - Functional safety - Safety instrumented systems for the process industry sector: This standard provides guidance on the design, implementation, and maintenance of safety instrumented systems (SIS) for the process industry sector. It can be used to assess risks related to the safety of industrial processes. API RP 752: Management of Hazards Associated with Location of Process Plant Permanent Buildings: This American Petroleum Institute recommended practice provides guidelines for identifying and evaluating hazards associated with the location of permanent process plant buildings. API RP 753: Management of Hazards Associated with Location of Process Plant Portable Buildings: This American Petroleum Institute recommended practice provides guidelines for identifying and evaluating hazards associated with the location of portable process plant buildings. NORSOK Standard S-001: Technical safety: This Norwegian Oil and Gas Association standard provides guidance on technical safety in the petroleum industry. It can be used to assess risks related to offshore petroleum operations. NFPA 652: Standard on the Fundamentals of Combustible Dust: This National Fire Protection Association standard provides requirements for managing the hazards associated with combustible dust. It can be used to assess risks related to combustible dust in industrial processes. These standards provide guidelines and requirements for risk assessment processes in different industries and contexts, and can help organizations effectively identify and manage potential hazards and risks.
Introducing Business Impact Assessment
Our team is working hard to bring this feature to Dmaze and we can't wait for you to try it out. Stay tuned for updates on it's progress.
Business Impact Assessment the way we see it
Business Impact Assessment (BIA) is a process that helps organizations understand the potential impact of disruptive events on their operations and critical business functions. The BIA process involves identifying key business processes and resources, assessing their criticality, and analyzing the potential impact of disruptions on these critical functions.
The BIA process typically includes a series of steps, such as conducting a risk assessment, identifying critical business functions and resources, defining recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs), and developing a recovery strategy. The BIA process helps organizations prioritize their recovery efforts and ensure that critical functions can be restored as quickly as possible after a disruptive event.
The BIA process is important for organizations of all sizes, as it helps to minimize the potential impact of disruptive events on their operations, finances, and reputation. By identifying and prioritizing critical business functions and resources, organizations can develop effective recovery strategies that minimize downtime and financial losses.
Overall, the BIA process is an essential component of any business continuity planning effort, as it provides a comprehensive understanding of the potential impact of disruptive events on critical business functions and resources. By conducting a BIA, organizations can proactively prepare for potential disruptions and ensure that they are well-positioned to recover quickly and effectively in the event of an unexpected event.
Business Impact Assessment Standards
There are several ISO standards that are relevant for Business Impact Assessment (BIA) processes. These include: ISO 22301:2019 - This standard specifies the requirements for a Business Continuity Management System (BCMS), which includes the BIA process. ISO 22301 provides a framework for organizations to develop and implement a BCMS that ensures the continuity of critical business functions in the event of disruptions. ISO 27031:2011 - This standard provides guidelines for Information and Communication Technology (ICT) readiness for business continuity. It includes the BIA process as a key component of ICT readiness for business continuity. ISO 22317:2015 - This standard provides guidelines for conducting a BIA. It includes the steps involved in conducting a BIA, such as identifying critical business functions, assessing the impact of disruptions, and defining recovery objectives. NFPA 1600:2022 - This is a standard developed by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) that provides guidelines for developing and implementing a comprehensive Emergency Management and Business Continuity Program. It includes the BIA process as a key component of the program. In addition to these ISO and NFPA standards, there are other standards that may be relevant to specific industries or sectors. For example, the financial industry may follow the ISO 22301 standard, but also adhere to the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council's (FFIEC) Business Continuity Planning (BCP) standards. Similarly, the healthcare industry may follow the ISO 22301 standard, but also adhere to the Joint Commission's Emergency Management (EM) standards. Overall, it is important for organizations to identify the relevant standards for their industry or sector and ensure that their BIA process aligns with these standards. This can help to ensure that the BIA process is effective, efficient, and compliant with industry best practices.
Introducing Chemical Risk Assessment
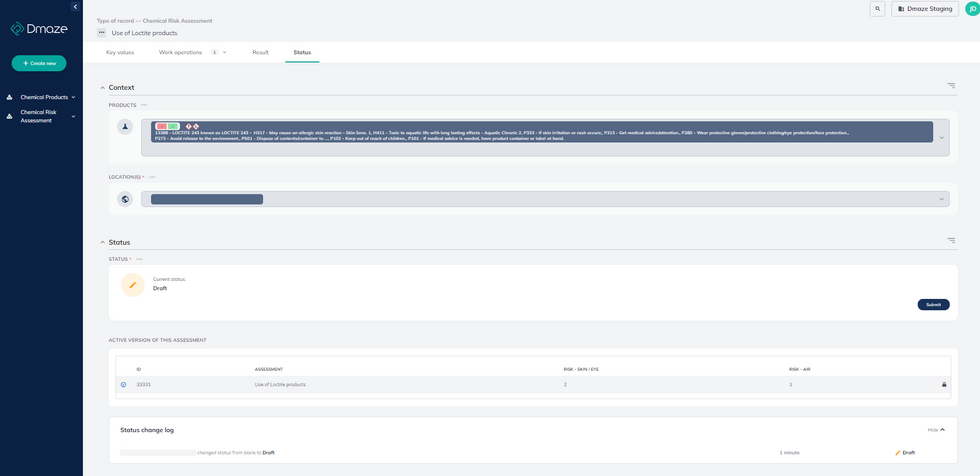
Chemicals are present in almost every workplace, and it is important to have a proper understanding of the risks they pose to the people who use them. This is where Dmaze comes in - our software is designed to help companies conduct an effective Chemical Risk Assessment, making it easier to ensure the safety of their employees.
Our software is easy to use and highly intuitive, allowing users to quickly and easily input the necessary data to generate an accurate risk assessment. The first step in this process is to provide a good description of the assessment to be performed. This includes information on the chemical being used, the purpose of using it, where the product will be used, and any other relevant details. By providing a comprehensive description of the assessment, Dmaze is able to generate a highly accurate risk assessment that takes into account all relevant factors.
The next step is to identify the activities the product is going to be used for. This includes information on the frequency and duration of the exposed work, as well as any technical or administrative barriers that are in place. Additionally, information on personal protective equipment (PPE) for both air and skin must be provided. By taking all of these factors into account, Dmaze is able to generate a highly accurate risk assessment that is tailored to the specific circumstances of each individual workplace.
One of the key features of Dmaze is our automatic risk analysis. Based on the information provided by the user, as well as the product's Safety Data Sheet (SDS), our software is able to automatically analyse the risks posed by the chemical being used. This information is then used to place the risk on the appropriate risk matrixes for skin/eye and air. Of course, the user always has the option to override the automatically generated risk if they feel it is necessary.
Overall, Dmaze is an essential tool for any company that is serious about ensuring the safety of their employees when working with chemicals. By providing a comprehensive risk assessment that takes into account all relevant factors, our software is able to help companies identify and mitigate any potential risks, making the workplace a safer and more secure environment for everyone involved. Whether you are a small startup or a large multinational corporation, Dmaze is the perfect solution for all your Chemical Risk Assessment needs.
Chemical Risk Assessment the way we see it
A Chemical Risk Assessment is a crucial process for any workplace where chemicals are used. This process involves identifying and evaluating the potential risks associated with the use of a particular chemical, and taking steps to minimize or eliminate those risks.
The first step in a Chemical Risk Assessment is to identify the chemical being used, as well as its properties and potential hazards. This information can usually be found in the product's Safety Data Sheet (SDS). It is important to review the SDS carefully, as it provides essential information on the appropriate handling and storage of the chemical.
Next, the workplace must be evaluated to determine how the chemical will be used, and what potential risks may be present. This includes identifying any potential sources of exposure, such as spills, leaks, or accidental contact with the skin or eyes. The frequency and duration of exposure must also be taken into account, as well as the potential consequences of exposure.
Once all potential risks have been identified, steps can be taken to minimize or eliminate them. This may include implementing engineering controls, such as ventilation systems or other safety equipment, or providing personal protective equipment (PPE) for employees. Training and education programs may also be necessary to ensure that employees are aware of the potential risks and know how to handle the chemical safely.
Finally, the Chemical Risk Assessment process should be reviewed regularly to ensure that it remains up-to-date and effective. This may include re-evaluating the risks associated with the chemical, as well as reviewing any new information that becomes available on its properties or hazards.
In summary, a Chemical Risk Assessment is a crucial process for any workplace where chemicals are used. By identifying and evaluating potential risks, and taking steps to minimize or eliminate them, companies can ensure the safety of their employees and create a secure and healthy work environment.
Chemical Risk Assessment Standards
There are several ISO standards that are relevant for a Chemical Risk Assessment process, including: ISO 45001:2018 Occupational health and safety management systems - Requirements with guidance for use: This standard provides guidelines for establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improving an occupational health and safety management system, which includes the identification of hazards, assessment of risks and implementation of controls. ISO 14001:2015 Environmental management systems - Requirements with guidance for use: This standard provides guidelines for establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improving an environmental management system, which includes the identification of environmental aspects and impacts, assessment of risks and implementation of controls. ISO/IEC 17025:2017 General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories: This standard provides guidelines for testing and calibration laboratories to demonstrate their competence, including requirements for quality management systems, personnel, equipment, and testing and calibration methods. OHSAS 18001:2007 Occupational health and safety management systems - Requirements: This standard provides guidelines for establishing, implementing, maintaining and continually improving an occupational health and safety management system, which includes the identification of hazards, assessment of risks and implementation of controls. In addition to these ISO standards, there are other relevant standards that may be applicable to specific industries or regions. For example, in the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established several standards related to chemical safety, including the Hazard Communication Standard (HCS) and the Process Safety Management (PSM) standard. It is important for companies to familiarize themselves with the relevant standards and regulations in their industry and region, and to ensure that their Chemical Risk Assessment process is in compliance with these requirements. This can help to ensure the safety of employees, prevent accidents and incidents, and reduce the risk of legal or financial liabilities.
Introducing DPIA
DPIA the way we see it
DPIA stands for Data Protection Impact Assessment, which is a process used to identify and minimize privacy risks associated with the processing of personal data. The DPIA process is an essential aspect of compliance with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and is designed to help organizations assess the potential impact that their data processing activities may have on individuals' privacy rights.
The DPIA process typically involves several stages, including:
Identifying the need for a DPIA: This involves assessing whether a DPIA is required based on the type of processing activity and the potential risks to individuals' privacy.
Describing the processing activity: This involves documenting the purpose of the processing activity, the type of personal data being processed, and the categories of individuals whose data will be processed.
Assessing the necessity and proportionality of the processing activity: This involves evaluating whether the processing activity is necessary to achieve the stated purpose and whether it is proportionate to the privacy risks identified.
Identifying and assessing privacy risks: This involves identifying potential privacy risks associated with the processing activity, such as the risk of unauthorized access, accidental disclosure, or misuse of personal data.
Evaluating measures to mitigate risks: This involves assessing the effectiveness of existing measures to mitigate privacy risks and identifying additional measures that can be implemented to reduce risks further.
Documenting and reviewing the DPIA: This involves documenting the DPIA process, including the results of the risk assessment and the measures taken to mitigate risks. The DPIA should be reviewed regularly to ensure that it remains up to date and relevant.
Overall, the DPIA process is an essential tool for organizations to ensure that they comply with data protection regulations and protect individuals' privacy rights.
DPIA Standards
There are several ISO standards and other standards that are relevant to DPIA processes. Some of the most important ones include: ISO/IEC 29134:2017 - Guidelines for privacy impact assessment: This standard provides guidelines for the conduct of privacy impact assessments, including the identification of privacy risks, the evaluation of the significance of these risks, and the identification of measures to mitigate these risks. ISO/IEC 27001:2013 - Information security management systems: This standard provides requirements for the establishment, implementation, maintenance, and continual improvement of an information security management system (ISMS), which is a key component of an effective DPIA process. ISO/IEC 27701:2019 - Privacy information management system: This standard provides guidelines for the establishment, implementation, maintenance, and continual improvement of a privacy information management system (PIMS), which is designed to support the management of privacy risks associated with the processing of personal data. NIST SP 800-53 Rev. 5 - Security and Privacy Controls for Information Systems and Organizations: This standard provides a catalog of security and privacy controls that can be used to manage risks associated with the processing of personal data. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): While not a standard, GDPR is a regulation that sets out the rules for the processing of personal data in the European Union. It requires organizations to conduct DPIAs in certain circumstances and provides guidance on how to conduct these assessments effectively. Overall, these standards and regulations can provide organizations with useful guidance and best practices for the conduct of effective DPIA processes. However, it is important to note that the specific requirements for DPIAs may vary depending on the nature of the processing activity and the applicable legal and regulatory framework.
Introducing Emergency Preparedness Assessment
Emergency Preparedness Assessment the way we see it
Emergency Preparedness Assessment is the process of evaluating an organization's ability to respond to and recover from potential emergencies or disasters. This process typically involves identifying potential hazards, assessing the risks associated with these hazards, and evaluating the organization's ability to respond to and recover from these risks.
During an Emergency Preparedness Assessment, an organization may examine its emergency management plan, evaluate the adequacy of its emergency response procedures, assess its training and exercise programs, review its communication protocols, and identify any gaps in its resources and capabilities.
The assessment process is critical for ensuring that an organization is prepared to respond to emergencies and disasters effectively. By identifying potential risks and gaps in preparedness, organizations can take steps to mitigate those risks and improve their overall emergency response capabilities.
Overall, an Emergency Preparedness Assessment should be a comprehensive and ongoing process, which involves all stakeholders, including employees, management, emergency response personnel, and community partners. It should be periodically reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the organization's operations, emerging threats, and new best practices in emergency management.
Emergency Preparedness Assessment Standards
There are several relevant ISO standards and other standards for Emergency Preparedness Assessment processes. Some of the most important ones include: ISO 22320:2018 - Societal Security - Emergency Management - Guidelines for Color-coded Alerts: This standard provides guidelines for developing and implementing color-coded alerts that can be used to communicate critical information during emergencies. ISO 22301:2019 - Societal Security - Business Continuity Management Systems - Requirements: This standard provides a framework for implementing a business continuity management system to help organizations prepare for, respond to, and recover from disruptive incidents. NFPA 1600: Standard on Disaster/Emergency Management and Business Continuity/Continuity of Operations Programs: This standard provides a comprehensive framework for emergency management, including the development of emergency plans, training and exercises, and business continuity planning. OSHA 1910.38: Emergency Action Plans: This standard requires employers to develop and implement emergency action plans to protect employees from emergencies. NIMS (National Incident Management System): This standard provides a framework for coordinating and managing emergency response activities across multiple jurisdictions and disciplines. These standards can help organizations ensure that their Emergency Preparedness Assessment processes are comprehensive, effective, and aligned with best practices in emergency management.
Introducing Environment Impact Assessment
Environment Impact Assessment the way we see it
The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) process is a systematic and scientific evaluation of the potential environmental impacts of a proposed project or development. The primary purpose of an EIA is to identify, predict, and evaluate the potential environmental effects of a proposed project and to develop measures to mitigate any negative impacts.
The EIA process typically involves several stages, including scoping, baseline data collection, impact analysis, and identification and evaluation of mitigation measures. The scoping stage involves identifying the scope of the assessment, including the project's physical and operational boundaries, potential impacts, and relevant environmental factors.
The baseline data collection stage involves collecting and analyzing data on the current environmental conditions in the project area. This data is used to establish a baseline against which potential impacts can be measured.
The impact analysis stage involves predicting the potential environmental effects of the proposed project based on the baseline data and the project's design and operation. This stage may include modeling, simulations, and other scientific techniques to assess the potential impacts.
Finally, the EIA process includes the identification and evaluation of measures to mitigate any negative impacts identified in the impact analysis stage. These mitigation measures may include design modifications, operational changes, or other actions to reduce the project's environmental impact.
Overall, the EIA process is an important tool for promoting sustainable development by identifying and addressing potential environmental impacts of proposed projects. It helps ensure that decision-makers have the information they need to make informed decisions and to balance economic, social, and environmental considerations.
Environment Impact Assessment Standards
There are several ISO standards and other standards that are relevant for Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) processes. Here are some of the most important ones: ISO 14001: This is the most widely recognized environmental management system standard, and it provides a framework for organizations to manage their environmental responsibilities. It can be used as a tool to help ensure that EIA processes are conducted in a systematic and effective manner. ISO 14004: This standard provides guidelines for the implementation of an environmental management system, including the planning, implementation, and monitoring of environmental management activities. It can help organizations to establish and maintain effective EIA processes. ISO 14005: This standard provides guidelines for the implementation of an environmental management system specifically for EIA processes. It provides guidance on the planning, design, implementation, and monitoring of EIA processes. ISO 19011: This is a standard for auditing management systems, including environmental management systems. It provides guidelines for conducting internal and external audits of environmental management systems, including EIA processes. The Equator Principles: These are a set of voluntary guidelines for banks and other financial institutions to assess and manage environmental and social risks associated with project finance. They provide a framework for ensuring that EIA processes are conducted in a transparent and effective manner. The International Association for Impact Assessment (IAIA) Guidelines: The IAIA is a professional organization for environmental and social impact assessment practitioners. They have developed a set of guidelines for conducting impact assessments, including EIA processes. These guidelines provide a comprehensive framework for conducting EIA processes that are in line with best practices. Overall, these standards provide a framework for ensuring that EIA processes are conducted in a systematic, effective, and transparent manner, and can help organizations to manage their environmental responsibilities and minimize their impact on the environment.
Introducing Ergonomic Assessments
Ensuring the safety and well-being of employees in the workplace is of utmost importance for any organization. To achieve this, companies must conduct ergonomic assessments to identify any hazards and risks that may be present in the workplace. This is where Dmaze comes in - a comprehensive software solution that revolutionizes the process of ergonomic assessments.
Dmaze is a state-of-the-art software that has been designed to make ergonomic assessments easier and more efficient. The software is user-friendly, and it can be customized to suit the specific needs of any organization. Dmaze allows companies to identify any hazards and risks that may be present in the workplace, including those related to lower extremities, back, shoulder/arm, hand/forearm, and neck.
One of the key benefits of using Dmaze is its ability to identify tasks that are risk assessed and provide an easy-to-understand visual representation of the risks. This allows organizations to take appropriate measures to mitigate any risks and ensure the safety of their employees. Dmaze can also identify barriers that are in place for heavy objects (>25 kg) that are handled regularly and for tasks that are heavy, monotonous, or require employees to work in twisted or bent positions.
In addition, Dmaze provides a good description of the work task being performed, making it easier for employees and employers to understand the nature of the work and the potential risks associated with it. The software can also identify any barriers in place for tasks that are heavy, monotonous, or must be performed with very twisted or bent positions.
Dmaze is a game-changer when it comes to ergonomic assessments. Its comprehensive features and user-friendly interface make it the perfect solution for any organization looking to improve workplace safety. With Dmaze, companies can minimize the risk of workplace injuries and accidents, and ensure the safety and well-being of their employees.
In conclusion, Dmaze is a must-have software for any organization that takes workplace safety seriously. It provides a comprehensive solution for ergonomic assessments and allows organizations to identify potential hazards and risks in the workplace. By choosing Dmaze, companies can improve workplace safety, minimize the risk of workplace injuries, and create a safer and more productive work environment.
Ergonomic Assessment the way we see it
Ergonomic assessments are an important part of workplace safety and can help organizations identify potential hazards and risks that may lead to workplace injuries and accidents. These assessments involve the evaluation of various work tasks and activities to identify any potential ergonomic risk factors that may cause musculoskeletal disorders or injuries to employees.
Ergonomic assessments typically include a review of the physical work environment, work tasks, and equipment used in the workplace. These assessments help organizations identify potential risk factors, such as awkward postures, repetitive motions, forceful exertions, and excessive vibration or pressure, that can contribute to workplace injuries and accidents.
By conducting ergonomic assessments, organizations can identify ways to modify work tasks or the physical work environment to reduce the risk of injury and improve employee comfort and productivity. Implementing ergonomic interventions can also result in reduced absenteeism, lower workers' compensation costs, and improved employee morale and job satisfaction.
Overall, ergonomic assessments are an important tool for organizations to identify potential hazards and risks in the workplace and ensure the safety and well-being of their employees. By conducting regular ergonomic assessments and implementing appropriate interventions, organizations can create a safer and healthier work environment for their employees, resulting in increased productivity, reduced injury rates, and improved employee satisfaction.
Ergonomic Assessment Standards
ISO standards related to ergonomic assessment are primarily concerned with human factors in the design of products, systems, and work environments to optimize human performance and well-being. Some of the most relevant ISO standards for ergonomic assessment are: ISO 9241: Ergonomics of Human-System Interaction - This standard provides guidelines for the design of interactive systems, including software and hardware, to ensure usability and efficiency for users. ISO 11226: Ergonomics - Evaluation of Static Working Postures - This standard specifies methods for evaluating the ergonomic risks associated with static working postures, including sitting, standing, and bending. ISO 11228: Ergonomics - Manual Handling - This standard provides guidelines for the assessment of the risks associated with manual handling tasks, including lifting, pushing, and pulling. ISO 6385: Ergonomic Principles in the Design of Work Systems - This standard provides a framework for designing work systems that optimize human performance and well-being by minimizing physical and mental stressors. ISO 15536: Ergonomics - Assessment of Speech Communication - This standard provides guidelines for the assessment of speech communication systems, including the design of interfaces and feedback mechanisms. ISO 20282: Ergonomics of Human System Interaction - Guidance on Human Centred Design for Interactive Systems - This standard provides a set of guidelines for human-centered design of interactive systems, including user interface design, task analysis, and usability testing. Other relevant standards for ergonomic assessment include ANSI/HFES 100-2007 Human Factors Engineering of Computer Workstations, OSHA Ergonomics Guidelines for Manual Material Handling, and the European Standard EN 1005-5 Safety of Machinery - Human Physical Performance.
Introducing GDPR Risk Assessment
GDPR Risk Assessment the way we see it
The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) requires that organizations assess and manage the risks associated with their processing of personal data. The risk assessment process involves identifying potential risks to the rights and freedoms of individuals, evaluating the likelihood and severity of those risks, and implementing appropriate measures to mitigate or eliminate them.
The GDPR risk assessment process typically involves the following steps:
Identify the scope of the assessment: Determine the scope of the assessment, including the types of personal data being processed, the purposes of the processing, and the data subjects involved.
Identify the risks: Identify potential risks to the rights and freedoms of individuals, including risks related to data security, data accuracy, data retention, and data processing activities.
Assess the risks: Evaluate the likelihood and severity of each identified risk, taking into account the nature, scope, context, and purposes of the processing activities.
Implement controls: Implement appropriate controls to mitigate or eliminate identified risks. This may include technical and organizational measures such as encryption, access controls, data minimization, and employee training.
Monitor and review: Continuously monitor and review the effectiveness of the implemented controls and update the risk assessment as necessary.
Overall, the GDPR risk assessment process is an essential part of GDPR compliance, and organizations must conduct it regularly to ensure ongoing compliance with the regulation.
GDPR Risk Assessment Standards
There are several ISO standards that are relevant for a GDPR risk assessment process. These include: ISO/IEC 27001:2013 - Information technology — Security techniques — Information security management systems — Requirements: This standard provides a framework for implementing and managing an information security management system (ISMS) and includes requirements for risk assessment and treatment. ISO/IEC 27005:2018 - Information technology — Security techniques — Information security risk management: This standard provides guidelines for conducting information security risk assessments and includes a methodology for identifying, analyzing, and evaluating risks. ISO/IEC 31000:2018 - Risk management — Guidelines: This standard provides guidelines for implementing a risk management framework and includes principles, framework, and process for managing risks. ISO/IEC 29134:2017 - Guidelines for privacy impact assessment: This standard provides guidelines for conducting privacy impact assessments (PIA) and includes a methodology for identifying, analyzing, and evaluating privacy risks. Other relevant standards include: NIST SP 800-53 - Security and Privacy Controls for Federal Information Systems and Organizations: This standard provides a catalog of security and privacy controls for federal information systems and organizations and includes requirements for risk assessment and management. BS 10012:2017 - Data protection: Specification for a personal information management system: This standard provides a framework for implementing and managing a personal information management system (PIMS) and includes requirements for risk assessment and treatment. In summary, ISO/IEC 27001, ISO/IEC 27005, ISO/IEC 31000, and ISO/IEC 29134 are the most relevant ISO standards for a GDPR risk assessment process, while NIST SP 800-53 and BS 10012 are also relevant for organizations seeking to comply with GDPR.
Introducing HAZID
HAZID is a critical process that every company must undertake to ensure the safety of its employees, protect the environment, and avoid costly incidents. However, traditional HAZID methods can be time-consuming and prone to errors. That's where Dmaze comes in.
Dmaze is the ultimate HAZID software that helps companies run an effective HAZID process with ease. With Dmaze, you can clearly describe the HAZID to be performed, focusing on description, assumptions, and objectives. The software enables you to identify potential hazards and analyze them based on probability and consequence. You can place each potential hazard in one of the matrixes for each consequence, such as People, Environment, Cost, Schedule, Production, or Reputation. Additionally, you can evaluate the knowledge strength and manageability of each potential hazard.
Dmaze software provides the ability to add a treatment plan and identify who is responsible for each task going forward. You can use the built-in AI function to suggest hazards and treatments, and configure workflows to ensure everything is done as agreed.
Dmaze simplifies the HAZID process, making it faster, more accurate, and more manageable. With Dmaze, you can rest assured that your company's safety and success are in good hands. Try Dmaze today and see the difference it can make for your business.
HAZID the way we see it
HAZID (Hazard Identification) is a systematic and structured process that helps identify and assess potential hazards associated with a project, process, or operation. It is an essential tool for risk management and helps to identify potential hazards that may cause harm to people, damage to the environment, loss of production, or damage to reputation.
HAZID is often used in high-risk industries such as oil and gas, chemical, and construction to identify potential hazards early in the design or planning stage. This helps companies to develop appropriate risk mitigation measures, reduce the likelihood of incidents, and minimize the impact of potential accidents or hazards.
The HAZID process involves a multidisciplinary team of experts who identify and evaluate potential hazards based on their experience, knowledge, and expertise. The team considers various factors, including the design, construction, operation, and maintenance of the project or process, as well as the potential consequences of each hazard.
HAZID is just one element of the broader risk management process, which includes risk assessment, risk control, and risk communication. By identifying potential hazards early in the project lifecycle, companies can develop appropriate risk management strategies and minimize the likelihood of accidents, incidents, or other adverse events.
HAZID Standards
There are several relevant ISO standards for a Hazard Identification (HAZID) process in risk management. These include: ISO 31000:2018 - Risk management - Guidelines: This is the international standard that provides a framework for managing risks in organizations. It is relevant for HAZID process as it provides guidance on identifying, analyzing, and evaluating risks. ISO 12100:2010 - Safety of machinery - General principles for design - Risk assessment and risk reduction: This standard provides guidance on risk assessment and risk reduction for machinery. It can be useful in a HAZID process when identifying and assessing risks associated with machinery. ISO 17776:2016 - Offshore and marine HAZID: This standard provides guidance on hazard identification in offshore and marine environments. It is relevant for HAZID process in the oil and gas industry, shipping, and other maritime activities. ISO 14971:2019 - Medical devices - Application of risk management to medical devices: This standard provides guidance on applying risk management to medical devices. It is relevant for HAZID process in the medical device industry. IEC 61882:2016 - Hazard and operability studies (HAZOP studies) - Application guide: This standard provides guidance on conducting HAZOP studies. It is relevant for HAZID process that involves HAZOP studies. IEC 61511:2016 - Functional safety - Safety instrumented systems for the process industry sector: This standard provides guidance on functional safety for safety instrumented systems (SIS) in the process industry sector. It can be useful in a HAZID process when identifying and assessing risks associated with SIS. It is important to note that these standards are not exhaustive and there may be other relevant standards depending on the specific industry or context in which the HAZID process is being conducted.
Introducing Operational Risk Assessment
Are you tired of lengthy and complex risk assessment processes that eat up precious time and resources? Say hello to Dmaze, the software that streamlines your risk assessment process and helps you make informed decisions.
Dmaze offers a comprehensive approach to operational risk assessment that focuses on identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential risks. With Dmaze, you can easily describe the assessment to be performed, including assumptions and objectives, and ensure that all stakeholders are on the same page.
Our software helps you identify risks quickly and efficiently, ensuring that you don't miss any potential hazards. Using advanced analytics and customizable risk matrices, Dmaze helps you analyze each risk's probability and consequences, enabling you to make data-driven decisions.
With Dmaze, you can easily categorize each risk based on its potential impact on people, the environment, cost, schedule, production, and reputation. Additionally, our software allows you to measure the knowledge strength and manageability of each risk, ensuring that you prioritize your efforts effectively.
Dmaze's treatment planning feature helps you identify the right actions to mitigate each risk, and our built-in AI function provides suggested risks and treatments to help you make informed decisions quickly.
Dmaze also comes with configurable workflows, ensuring that every step of the assessment process is followed consistently and efficiently. With Dmaze, you can rest assured that your operational risk assessment process is in good hands.
Don't waste any more time on ineffective risk assessment processes. Try Dmaze today and take the first step towards effective risk management.
Operational Risk Assessment the way we see it
Operational Risk Assessment is a crucial process for any business, regardless of its size or industry. It involves identifying, evaluating, and managing risks that could affect an organization's ability to achieve its objectives. These risks can arise from various sources, such as technology failures, human errors, regulatory changes, natural disasters, and more.
The purpose of Operational Risk Assessment is to enable businesses to understand their exposure to risks and take proactive measures to mitigate them. By conducting a thorough assessment, businesses can identify potential risks and assess their likelihood and potential impact. This information can then be used to develop strategies to manage and mitigate those risks, ensuring business continuity and protecting the organization's assets and reputation.
An effective Operational Risk Assessment process involves a structured and systematic approach, which typically includes several steps, such as risk identification, risk analysis, risk evaluation, risk treatment, and risk monitoring. It also requires input from various stakeholders across the organization, such as business units, operations, compliance, and risk management teams.
Overall, an effective Operational Risk Assessment process can help businesses anticipate and manage risks more effectively, improve decision-making, and enhance their overall resilience in the face of uncertainty and change.
Operational Risk Assessment Standards
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) has developed several standards related to risk management, including operational risk assessment. The most relevant ISO standards for an Operational Risk Assessment process are: ISO 31000:2018 - Risk management -- Guidelines This standard provides a framework for risk management and includes principles, framework, and a process for managing risk. It is applicable to all types of organizations and provides guidance on the management of risks faced by an organization. ISO/IEC 31010:2019 - Risk management -- Risk assessment techniques This standard provides a variety of risk assessment techniques that can be used to identify, analyze, and evaluate risks. It includes methods for both qualitative and quantitative risk assessment. ISO/IEC 27005:2018 - Information technology -- Security techniques -- Information security risk management This standard provides guidance on the assessment and management of information security risks. It includes a risk assessment process that can be adapted to different organizations and industries. Other relevant standards include: COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission) - Enterprise Risk Management Framework This framework provides a comprehensive approach to risk management that can be applied to any organization. It includes an assessment of the organization's internal and external environments, as well as the identification, analysis, and management of risks. NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) - Risk Management Framework This framework provides a structured approach to risk management that is specifically tailored to information technology systems. It includes steps for categorizing information and systems, selecting and implementing security controls, assessing the effectiveness of those controls, and monitoring the ongoing security posture of the organization. OHSAS (Occupational Health and Safety Assessment Series) 18001:2007 - Occupational health and safety management systems -- Requirements This standard specifies requirements for an occupational health and safety management system (OHSMS). It includes a risk assessment process that can be used to identify and manage hazards in the workplace. OHSAS 18001 has been superseded by ISO 45001:2018, which includes a similar risk assessment process. Overall, these standards can provide a helpful framework for conducting an Operational Risk Assessment process as part of a broader risk management program. It is important to note that each organization may have unique risks and risk management needs, and these standards should be tailored to fit the specific context of the organization.
Introducing PEST Assessment
Our team is working hard to bring this feature to Dmaze and we can't wait for you to try it out. Stay tuned for updates on it's progress.
PEST Assessment the way we see it
PEST analysis, also known as PESTLE analysis or sometimes STEEPLE analysis, is a framework used to analyze the external factors that may affect a business or organization. The acronym PEST stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological, which are the four main categories of external factors that may impact a business.
Political factors include government policies, regulations, and political stability in a country or region. Economic factors refer to the economic conditions, such as inflation, interest rates, and economic growth, which can affect the buying power and behavior of customers. Social factors are related to the cultural and demographic trends, such as attitudes, beliefs, and lifestyles of the population. Finally, technological factors include the advancements in technology that can affect the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
PEST analysis can be used to identify opportunities and threats, assess market potential, and inform strategic decision-making. It can also help businesses anticipate and adapt to changes in the external environment. However, it is important to keep in mind that the results of a PEST analysis are influenced by various factors such as the industry, geography, and timeframe being analyzed.
PEST Assessment Standards
ISO standards do not directly address PEST (Political, Economic, Social, and Technological) assessments, as these assessments are a strategic planning tool rather than a process that requires standardization. However, there are several ISO standards and other frameworks that can be relevant to a PEST assessment process, as they provide guidance on various aspects of strategic planning. Here are some of the most relevant ISO standards and other frameworks: ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System - This standard provides guidelines for implementing and maintaining a quality management system, which can help organizations ensure that their PEST assessments are conducted in a structured and consistent manner. ISO 31000:2018 Risk Management - This standard provides guidelines on how to identify, assess, and manage risks that may affect an organization's strategic objectives, which can help organizations identify and mitigate risks related to PEST factors. ISO 22301:2019 Business Continuity Management - This standard provides guidance on how to plan, implement, and maintain a business continuity management system, which can help organizations prepare for and respond to disruptions related to PEST factors. SWOT Analysis - SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) Analysis is a commonly used framework for strategic planning that can help organizations assess their internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats, which can be useful for identifying and analyzing PEST factors. PESTLE Analysis - PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental) Analysis is a framework that can help organizations identify and analyze external factors that may affect their business operations and strategic objectives, which can be useful for conducting a comprehensive PEST assessment. Porter's Five Forces Analysis - This framework provides a structured approach for analyzing the competitive environment in which an organization operates, which can be useful for assessing the impact of PEST factors on an organization's competitive position. Overall, while there are no specific ISO standards for PEST assessments, organizations can use a combination of the above frameworks and standards to conduct a comprehensive and structured assessment of the external factors that may affect their strategic objectives.
Introducing Project Risk Assessment
Are you tired of ineffective and time-consuming project risk assessments? Look no further than Dmaze! Our software is specifically designed to streamline the risk assessment process, making it easier for companies to identify, analyze, and mitigate potential risks.
With Dmaze, you'll get a comprehensive description of the assessment to be performed, along with the ability to identify risks based on project phases. Our software also allows for detailed analysis of each risk and ensures that they are accurately placed in the risk matrix.
But that's not all! Dmaze also offers pre- and post-mitigation probability and consequence assessments for each risk, with consequence types including asset and operation, commercial, environmental, financial, injury/health, legal & contractual, schedule, and technical.
Our software even includes a treatment plan feature, with the ability to assign responsibilities and track progress going forward. And if you need suggestions for risks and treatments, our built-in AI function can provide valuable insights.
Dmaze also includes configurable workflows to ensure that everything is done as agreed, providing a hassle-free experience for companies looking to improve their project risk assessment process.
Don't settle for mediocre risk assessments. Upgrade to Dmaze and ensure the success of your projects!
Project Risk Assessment the way we see it
Project Risk Assessment is a critical process for any organization involved in project management. It involves identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing potential risks that may impact a project's outcome, and developing strategies to mitigate or manage those risks.
The objective of Project Risk Assessment is to minimize the negative impact of potential risks while maximizing opportunities for success. Risks can arise from various sources such as technological factors, external factors, market factors, and organizational factors. Therefore, it is essential to assess risks in all stages of a project to ensure that potential risks are identified and addressed proactively.
Effective Project Risk Assessment requires a systematic approach and involves collaboration between different stakeholders involved in the project. The process involves identifying and classifying risks, evaluating their likelihood and impact, developing mitigation strategies, and monitoring and reviewing risks continuously throughout the project's lifecycle.
An effective Project Risk Assessment can help organizations avoid costly and time-consuming project delays, budget overruns, and damage to their reputation. By identifying potential risks early in the project, organizations can develop strategies to minimize their impact and ensure the project's success.
Overall, Project Risk Assessment is a crucial process for any organization involved in project management, and investing in tools and software like Dmaze can help organizations streamline the process and manage risks more effectively.
Project Risk Assessment Standards
There are several relevant standards for project risk assessment and risk management. Some of the most widely recognized and applicable standards are: ISO 31000:2018 - Risk management -- Guidelines: This standard provides guidelines and principles for effective risk management practices. It covers the entire risk management process, including risk identification, analysis, evaluation, treatment, monitoring, and communication. ISO/IEC 31010:2019 - Risk management -- Risk assessment techniques: This standard provides guidance on various risk assessment techniques that can be used to identify, evaluate and prioritize risks. It includes quantitative, qualitative and semi-quantitative methods. ISO 22301:2019 - Societal security -- Business continuity management systems -- Requirements: This standard specifies the requirements for a business continuity management system (BCMS), which includes risk assessment and management as an integral part. It provides a framework for organizations to manage and minimize the impact of disruptive incidents. ISO/IEC 27001:2013 - Information technology -- Security techniques -- Information security management systems -- Requirements: This standard specifies the requirements for an information security management system (ISMS), which includes risk assessment and management as an essential part. It provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information so that it remains secure. COSO ERM Framework: This framework provides a comprehensive and integrated approach to enterprise risk management (ERM). It covers eight interrelated components that provide a holistic view of risk management, including internal environment, objective setting, event identification, risk assessment, risk response, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring. PMI Risk Management Standard: This standard provides a framework for managing project risks. It covers the entire project risk management process, including risk identification, analysis, response planning, implementation, and monitoring. IEC 31000:2009 - Risk management - Principles and guidelines: This standard provides a general framework for risk management across all types of organizations, industries, and activities. It covers risk assessment, risk treatment, communication, and monitoring. These standards can provide a comprehensive framework for effective risk management practices. However, organizations should choose the most appropriate standards that align with their industry, business model, and specific risk management needs.
Introducing Risk and Vulnerability Assessment
Do you want to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in your business and take effective measures to manage them? Look no further than Dmaze! Our powerful software is designed to help businesses conduct risk and vulnerability assessments with ease, making sure that all risks are properly analyzed and managed.
With Dmaze, you can expect a comprehensive assessment that covers everything from identifying risks to developing treatment plans. Our software is equipped with a built-in AI function that suggests potential hazards and treatments based on your data, making the process even easier.
Our software allows you to place each potential hazard in one of our customized risk matrixes, based on its probability and consequence. You can assess the impact on people, environment, cost, schedule, production, and reputation, ensuring that you have a complete understanding of the risks your business faces.
At Dmaze, we understand that knowledge strength and manageability are critical factors in risk assessment. That's why our software takes these factors into account when analyzing risks and developing treatment plans.
Our software comes with built-in configurable workflows that ensure everything is done as agreed, so you can rest assured that your business is protected from potential risks and vulnerabilities.
So, if you want to take a proactive approach to risk management and ensure the safety and security of your business, try Dmaze today!
Risk and Vulnerability Assessment the way we see it
Risk and Vulnerability Assessment (RVA) is a vital process for any organization that wants to identify and manage potential risks that could negatively impact its operations. The main goal of RVA is to identify and assess vulnerabilities and threats that may exist in an organization's environment, including its infrastructure, systems, people, and processes.
RVA involves a comprehensive and systematic evaluation of all potential risks and threats, including natural disasters, cyber-attacks, physical security breaches, and human error, among others. It requires a detailed understanding of the organization's operations, assets, and objectives, as well as its regulatory and compliance requirements.
The process of RVA typically involves several steps, including identifying and assessing risks, analyzing the likelihood and impact of those risks, and developing mitigation strategies and contingency plans. It requires a collaborative approach that involves various stakeholders, including management, technical experts, and risk management professionals.
Effective RVA is essential to help organizations proactively manage and mitigate potential risks, thereby reducing the likelihood and impact of adverse events. By identifying and addressing vulnerabilities and threats before they materialize, RVA helps organizations to enhance their resilience, protect their reputation, and ensure business continuity.
Risk and Vulnerability Assessment Standards
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) has published several standards that are relevant to Risk and Vulnerability Assessment in Risk Management. Some of the most relevant ISO standards are: ISO 31000:2018 - Risk management - Guidelines This standard provides principles, framework, and a process for managing risk in organizations. It also helps organizations to develop a risk management plan and identify, assess, treat, and monitor risks. ISO/IEC 27001:2013 - Information technology - Security techniques - Information security management systems - Requirements This standard specifies the requirements for an information security management system (ISMS) to manage and protect information assets. It includes guidelines for risk assessment and treatment. ISO/IEC 27005:2018 - Information technology - Security techniques - Information security risk management This standard provides guidelines for information security risk management, including risk assessment and risk treatment. It also includes the selection of appropriate risk analysis methods and risk evaluation techniques. ISO 22301:2019 - Security and resilience - Business continuity management systems - Requirements This standard provides requirements for developing and implementing a business continuity management system (BCMS). It includes guidelines for risk assessment, risk treatment, and business impact analysis. ISO 22320:2018 - Security and resilience - Emergency management - Guidelines for incident management This standard provides guidelines for incident management, including risk assessment, planning, and response. ISO 45001:2018 - Occupational health and safety management systems - Requirements with guidance for use This standard provides requirements and guidelines for implementing an occupational health and safety management system (OH&SMS). It includes guidelines for risk assessment and risk treatment in the context of OH&S. Apart from these ISO standards, there are other standards and frameworks that can be used in the Risk and Vulnerability Assessment process in Risk Management, such as NIST SP 800-30, ISF Standard of Good Practice for Information Security, and COBIT 2019.
Introducing Stakeholder Assessment
Stakeholder Assessment the way we see it
Stakeholder assessment is a process of identifying and analyzing the individuals, groups, or organizations that have an interest or stake in a particular project, program, or organization. The purpose of stakeholder assessment is to understand the needs, expectations, and concerns of various stakeholders and to develop strategies to effectively engage and manage them.
The stakeholder assessment process typically involves the following steps:
Identifying stakeholders: This step involves identifying all the potential stakeholders who may be affected by or have an interest in the project or program.
Analyzing stakeholders: Once the stakeholders are identified, the next step is to analyze their needs, expectations, concerns, and attitudes towards the project or program. This analysis can be done through interviews, surveys, focus groups, or other research methods.
Prioritizing stakeholders: Based on the analysis, stakeholders can be prioritized based on their level of influence, importance, and interest in the project or program.
Developing engagement strategies: After prioritizing stakeholders, the next step is to develop strategies to effectively engage and manage them. These strategies may include communication plans, stakeholder meetings, outreach activities, or other methods of engagement.
Monitoring and evaluating stakeholder engagement: The final step is to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of stakeholder engagement strategies and make adjustments as needed.
Overall, stakeholder assessment is a critical process that can help organizations build effective relationships with their stakeholders and ensure the success of their projects and programs.
Stakeholder Assessment Standards
There are several ISO standards and other standards that may be relevant for a stakeholder assessment process, depending on the specific context and purpose of the assessment. Here are some examples: ISO 26000: This standard provides guidance on social responsibility and includes a section on stakeholder engagement. It emphasizes the importance of identifying and engaging with stakeholders and provides guidance on how to do so effectively. ISO 31000: This standard provides guidelines for risk management and includes a section on stakeholder engagement. It emphasizes the importance of identifying stakeholders and their needs and concerns, and involving them in the risk management process. AA1000 Stakeholder Engagement Standard: This is a standard developed by AccountAbility and provides guidance on stakeholder engagement for organizations. It emphasizes the importance of engaging stakeholders in a meaningful and transparent way and provides a framework for doing so. Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards: These are a set of standards for sustainability reporting that include a section on stakeholder engagement. They provide guidance on how to identify and engage stakeholders, and how to report on stakeholder engagement activities. IFC Performance Standards: These are a set of environmental and social performance standards developed by the International Finance Corporation (IFC). They include a section on stakeholder engagement and provide guidance on how to identify and engage stakeholders in a way that is culturally appropriate and respectful. OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises: These guidelines provide recommendations for responsible business conduct and include a section on stakeholder engagement. They emphasize the importance of engaging with stakeholders in a way that is transparent and inclusive, and provides guidance on how to do so effectively. Overall, the choice of standards for a stakeholder assessment process will depend on the specific context and purpose of the assessment, as well as the goals and values of the organization conducting the assessment.
Introducing Security Risk Management in Dmaze
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, staying ahead of threats is paramount. That's where Dmaze steps in, your trusted partner in achieving unparalleled Security Risk Management excellence. Our software redefines the way companies safeguard their assets, identify threats, and assess risks by seamlessly integrating three powerful templates: Risk Assessment, Threat Assessment, and Asset Assessment.
In the Asset Assessment module, we lay the cornerstone of your security strategy:
-
Precision at Its Best: Craft a comprehensive assessment with a sharp focus on title, description, responsible unit, and location.
-
Asset Unveiling: Identify, map, and evaluate all assets with details on dependencies, redundancies, descriptions, and overall criticality.
-
Streamlined Workflows: Our software features customizable workflows, ensuring every task aligns with your security objectives.
The Threat Assessment template empowers you to navigate the threat landscape:
-
Defining the Threatscape: Articulate assessments with precision through titles, descriptions, organizational units, and locations.
-
Threat Profiling: Identify threats comprehensively, including stakeholders, intentions, capabilities, known incidents, evaluations, and threat levels.
-
Workflow Mastery: Enjoy the ease of configurable workflows that keep your security processes on track.
In the Risk Assessment module, we tie it all together for a holistic view:
-
The Assessment Blueprint: Define assessments with clarity, including titles, descriptions, analysis purpose, scope, participants, organizational units, and locations.
-
Integration: Connect Asset Assessments and Threat Assessments seamlessly, fostering a comprehensive understanding of your security posture.Seamless
-
Scenario Mapping: Identify scenarios in detail, covering titles, descriptions, related assets, related threats, probabilities, consequences, security strategies, vulnerability assessments, and summaries.
-
Effortless Workflows: Our software's configurable workflows ensure adherence to your security protocols.
-
Treatment and Accountability: Assign responsibility with precision, outlining a treatment plan that ensures a secure future.
With Dmaze, security risk management becomes more than a task; it becomes a strategic advantage. Elevate your security posture, streamline your processes, and embrace the future of safeguarding your assets. Trust in Dmaze, where security meets innovation, and risk management is a breeze.
Security Risk Management the way we see it
Security Risk Management is a critical and strategic approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that can potentially harm an organization's information, assets, operations, and reputation. It plays a fundamental role in ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of an organization's resources in an increasingly complex and interconnected world.
Here are some key points to understand about Security Risk Management:
-
Risk Identification: The process begins with identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities that could affect an organization's security. Threats can be anything from cyberattacks and natural disasters to insider threats and regulatory changes. Vulnerabilities are weaknesses that could be exploited by these threats.
-
Risk Assessment: Once identified, risks are assessed in terms of their likelihood and potential impact. This assessment helps organizations prioritize which risks to address first and allocate resources accordingly.
-
Risk Mitigation: After assessing risks, organizations develop strategies to mitigate or reduce them. This can involve implementing security controls, policies, and procedures to minimize vulnerabilities and protect against threats. The goal is to reduce the risk to an acceptable level.
-
Risk Monitoring: Security Risk Management is an ongoing process. Risks are dynamic, and new threats can emerge, so continuous monitoring is essential. Organizations should regularly review and update their risk assessments and mitigation strategies to adapt to changing circumstances.
-
Compliance and Regulations: Many industries have specific regulations and compliance requirements related to security and risk management. Organizations must ensure they adhere to these regulations to avoid legal and financial consequences.
-
Cybersecurity: In today's digital age, cybersecurity is a significant component of Security Risk Management. Protecting digital assets and sensitive information from cyber threats is a top priority for organizations worldwide.
-
Business Continuity: Effective Security Risk Management also includes planning for business continuity in case of disruptions. This involves creating disaster recovery and incident response plans to minimize downtime and maintain essential operations.
-
Communication and Training: Employees play a crucial role in security risk management. Organizations should invest in employee training and awareness programs to ensure that everyone understands their role in maintaining security and responding to incidents.
-
Risk Tolerance: Organizations have different risk tolerance levels based on their industry, size, and objectives. Some industries, such as finance and healthcare, have very low tolerance for risk, while others may be more flexible. Understanding and defining risk tolerance is essential.
-
Strategic Asset Protection: Ultimately, Security Risk Management aims to protect an organization's most valuable assets, including data, intellectual property, physical infrastructure, and reputation. It's an integral part of an organization's overall risk management strategy.
In summary, Security Risk Management is a comprehensive and ongoing process that helps organizations proactively identify, assess, and mitigate risks to protect their assets, operations, and stakeholders from various threats. It's a critical aspect of modern business and requires a proactive, adaptable, and strategic approach to stay ahead of evolving risks and challenges.
There are several international standards and frameworks relevant to Security Risk Management that organizations can refer to for guidance and best practices. Here is a list of some of the most prominent standards and frameworks: •ISO 27001: ISO/IEC 27001 is a widely recognized international standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). It provides a systematic approach to managing information security risks. •ISO 31000: ISO 31000 is an international standard for Risk Management. While it is not specific to security, it provides a comprehensive framework for managing all types of risks, including security risks. •NIST Cybersecurity Framework: Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the United States, this framework provides guidelines for improving cybersecurity risk management. •NIST SP 800-53: This NIST publication provides security controls and guidelines for federal information systems and organizations in the United States. It's widely referenced in government and industry. •COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies): COBIT is a framework developed by ISACA that focuses on governance and management of enterprise IT, including security risk management. •CIS (Center for Internet Security) Controls: The CIS Controls provide a prioritized set of actions for organizations to improve cybersecurity posture. They are widely adopted for security risk management. •PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): This standard is applicable to organizations that handle credit card transactions. It sets security requirements for protecting cardholder data. •ISO 22301: ISO 22301 is the international standard for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS). It is relevant for security risk management as it addresses resilience and continuity in the face of disruptions. •ISO 28000: This standard focuses on supply chain security management systems, addressing security risks related to the movement of goods and materials. •ISO 22316: ISO 22316 provides guidance on organizational resilience, including aspects related to risk management and security. •ISO 45001: ISO 45001 is the international standard for Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems (OHSMS). While it primarily focuses on safety, it can overlap with security in certain areas, especially in critical infrastructure protection. •ANSI/ASIS Standards: ASIS International develops various security-related standards, such as those related to physical security, investigations, and risk management. •IEC 62443: This series of standards from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) addresses cybersecurity for industrial control systems (ICS) and is relevant for organizations in critical infrastructure sectors. •HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): HIPAA sets security and privacy standards for healthcare organizations in the United States. •GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): While primarily focused on data protection and privacy, GDPR also has security implications and requires organizations to manage risks related to personal data. These standards and frameworks offer valuable guidance and best practices for organizations looking to establish robust Security Risk Management processes and enhance their overall security posture. The specific standards relevant to an organization may vary depending on its industry, geographical location, and regulatory requirements.
Introducing Working Environment Initial Assessment (WERA)
Are you tired of struggling with a lack of clarity and organization in your company's Working Environment Initial Assessment (WERA) process? Do you want to improve the safety and well-being of your employees while streamlining your assessment workflow? Look no further than Dmaze - the all-in-one software solution for WERA assessments.
At its core, Dmaze is designed to make the WERA process as clear and efficient as possible. With its easy-to-use interface, you can quickly and easily input all the necessary information for each assessment, including the title, description, area, WERA type, unit, start and end dates, persons contributing, verifier (user), status, and responsible person. This allows for a comprehensive view of all assessments at a glance, making it simple to manage and track progress.
But Dmaze goes far beyond just organizing data - it also helps identify and assess the specific activities that make up each assessment. With detailed descriptions of each activity, planned barriers, and work performed by, you can gain a full understanding of each step involved in the assessment process. Additionally, the software allows you to add important information about potential hazards associated with each activity, including ergonomics, illumination, climatic conditions, chemicals, vibrations, noise, radiation, and shift work.
One of the key features of Dmaze is its risk ranking system. For each activity, the software automatically calculates and displays the risk evaluation before and after mitigation. This allows you to quickly assess the level of risk associated with each activity, and take steps to reduce it as necessary. The system also includes comments for potential health hazards and exposure assessments, providing a more complete picture of the risks involved in each activity.
Of course, simply identifying risks is not enough - Dmaze also allows you to take action to mitigate those risks. For each activity, you can add actions to be taken, ensuring that the assessment process is as safe and efficient as possible. And with built-in configurable workflows, you can be sure that everything is being done according to the agreed-upon plan.
In short, Dmaze is the ultimate software solution for Working Environment Initial Assessment (WERA) assessments. By providing a clear and organized view of each assessment, identifying and assessing potential hazards, and allowing for easy action-taking, it streamlines the entire process while ensuring the safety and well-being of your employees. Try it out today and see the difference it can make for your company!
Working Environment Initial Assessment (WERA) the way we see it
Working Environment Initial Assessment (WERA) is a crucial process for any organization that wants to ensure the safety and well-being of its employees. WERA is typically conducted to identify potential hazards in the workplace, evaluate the level of risk associated with those hazards, and take action to mitigate those risks.
The WERA process can be quite complex, as it involves identifying all potential hazards associated with a particular task or job, assessing the risks associated with those hazards, and then taking steps to reduce or eliminate those risks. This can involve a range of factors, including ergonomics, illumination, climatic conditions, chemicals, vibrations, noise, radiation, and shift work.
A well-conducted WERA can have a number of benefits for both employees and employers. By identifying and mitigating potential hazards, organizations can reduce the risk of workplace accidents, injuries, and illnesses, and create a safer and more productive work environment. Additionally, a thorough WERA can help organizations comply with local and national regulations related to workplace safety.
However, conducting a WERA can be a complex and time-consuming process, which is where Dmaze comes in. By streamlining the entire process and providing a clear and organized view of each assessment, Dmaze makes it easy for organizations to conduct a thorough WERA and ensure the safety and well-being of their employees.
Working Environment Initial Assessment (WERA) Standards
ISO Standards and other relevant standards for WERA can provide guidelines and requirements for conducting a comprehensive and effective WERA. Some of the most commonly used standards include: ISO 45001: Occupational health and safety management systems - Requirements with guidance for use: This ISO standard specifies requirements for an occupational health and safety (OH&S) management system and provides guidance for its use. It can be used as a framework for implementing a WERA and ensuring compliance with OH&S regulations. ISO 14001: Environmental management systems - Requirements with guidance for use: While not specifically related to WERA, ISO 14001 provides guidelines for implementing an environmental management system, which can be useful for assessing the environmental impact of workplace activities as part of a comprehensive WERA. ISO 9001: Quality management systems - Requirements: ISO 9001 provides requirements for implementing a quality management system, which can be useful for ensuring the quality and consistency of a WERA. OHSAS 18001: Occupational health and safety management systems: This standard provides requirements for an OH&S management system, similar to ISO 45001, and can also be used as a framework for implementing a WERA. ANSI/ASSP Z590.3: Prevention through Design: Guidelines for addressing occupational hazards and risks in design and redesign processes: This American National Standard provides guidelines for addressing occupational hazards and risks during the design and redesign process, which can be useful for incorporating risk assessment into the WERA process. IEC 62366: Medical devices - Application of usability engineering to medical devices: This International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard provides guidelines for conducting a usability engineering process, which can be useful for assessing the usability and safety of workplace equipment as part of a WERA. Overall, these standards can provide useful guidance and requirements for conducting a comprehensive WERA and ensuring the safety and well-being of employees in the workplace.